Arthritis
Contents
Description & Causes
Arthritis is the result of inflammation, pain and soreness of the joints. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the two most common types of this disease.
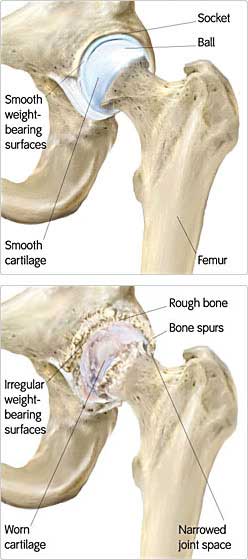
Osteoarthritis develops as a result of the continuous wearing away of the cartilage in a particular joint. Cartilage, is a smooth, soft, protective tissue that covers the ends of the bones at the joints. This tissue may become thin and disappear through excessive wear, as seen most often in the elderly. When enough cartilage has worn away, the rough surfaces of the bones rub together, causing not only pain, but stiffness. Weight-bearing joints such as the hips and knees are most affected. Symptoms are intensified during damp weather, upon rising from sleep in the morning, or after strenuous activity.
Rheumatoid arthritis not only affects a particular joint, but the body in its entirety. It destroys not only the cartilage and tissues around the joints, but often the bone surfaces themselves. The body naturally replaces the damaged tissue with scar tissue. This replacement causes the spaces between the joints to become narrow and eventually fuse together, resulting in painful deformities that may affect the quality of life. The result can be crippling, and often includes swelling and joint pain, fatigue, anemia, weight-loss and fever. Symptoms may disappear and recur at a later date.
Prevention & Treatment
Exercise is extremely important in both the prevention and treatment of arthritis, because unused joints tend to "dry out" and stiffen. Good posture is also important, as poor posture can cause body weight to be unevenly distributed, placing unnecessary stress on the joints and ultimately resulting in pain.
Those who are over-weight or obese are more prone to arthritic conditions. A well-balanced diet is is mandatory, as the body needs all the available nutrients for repair.
Vitamins & Nutrients
Following are some of the vitamins and nutrients that may be beneficial in the treatment of arthritis.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Cetyl Myirstoleate
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B complex
- Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B12
- Niacin
- Folic acid
- Vitamin B5 (panthothenic acid)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin F
- Bioflavonoids
- Calcium
- Iodine
- Lecithin
- Magnesium
- MSM (Methylsulphonylmethane)
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Sulfur
- Protein
- Glucosamine Sulfate
- Chondroitin
- Omega 3
- Probiotics
- Rosehips
- Pycnogenol
Beneficial Herbs
- Bromelain
- Devil's Claw
- Yucca
- Horsetail
- Alfalfa
- Yarrow
- Capsicum
- Valerian
- White Willow
- Burdock
- Frankincense
- Feverfew
Related Discussions
- What's Good For Arthritis?
- Rheumatoid Arthritis 'on the rise in women'
- May is Arthritis Awareness Month