Gout
Contents
Description & Causes
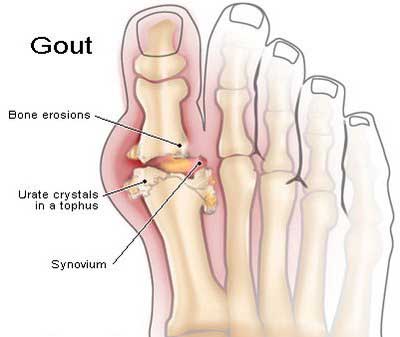
Gout is a metabolic disturbance characterized by an excessive amount of uric acid in the blood and deposits of uric acid salts inside the tissues around the joints. This disease can occur in any joint in the body including fingers, toes, heels, knees, hands or ears.
When certain crystals are formed as an end product of improper protein metabolism, gout can be the result. These crystals which are deposited in a joint, form a bump or growth which creates irritation and inflammation, causing an attack. Although the exact cause isn't known, this condition appears to be hereditary. However, factors such as obesity, improper diet and aging increase the susceptibility of gout.
Excessive alcohol consumption, a large meal or any physical or emotional stress can promote an attack of gout.
Symptoms & Treatment
A gout attack can begin with pain in the inflamed joint, which may spread to other joints in the body. Pain is usually greatest in early morning, and subsides later in the day. Episodes may last from five to twelve days, and then recur months later.
Treatment for gout usually involves encouragement of regular exercise, rest and diet. Also, supplements which decrease inflammation are recommended. Diet should be moderate in protein, and low in fats. Foods such as organ meats, which contain a high amount of purine, forerunner of uric acid, should be avoided.
Adequate intake of fluids is also advised to help prevent the accumulation of gout-producing crystals in the kidneys. A gradual weight reduction program for over-weight individuals will help to prevent gout attacks.
Beneficial Vitamins & Nutrients
Some vitamin, minerals and nutrients which are useful in the treatment of gout are:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B complex
- Vitamin B5 (panthothenic acid)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Calcium
- Iodine
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Omega 3 (fish oil)
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Coconut oil
- Cherry juice (dark, black)
Helpful Herbs
Some herbs that are valuable in both the prevention and treatment of gout are:
- Alfalfa
- Angelica
- Birch
- Burdock
- Celery (seed)
- Chickweed
- Comfrey
- Devil's Claw
- Fennel
- Ginger
- Hydrangea
- Nettle
- Queen of the Meadow
- Red Clover
- Rosemary
- Safflower
- Saffron
- Skullcap
- Thyme
- White Willow